Published June 2021
Biodegradable polymers, as defined in this report, are bio-based or synthetic polymers that undergo microbial decomposition to carbon dioxide and water in industrial compost facilities. A few of these polymers decompose in backyard compost bins or in soil, freshwater, or saltwater.
Major biodegradable polymers include polylactic acid (PLA); polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), including polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) and related copolymers; cellulose diacetate; regenerated cellulose; copolyesters such as polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) and polybutylene succinate adipate (PBSA); polybutylene succinate (PBS); polycaprolactone (PCL); polyglycolic acid (PGA); and starch compounds (mixtures of starch and other biodegradable polymers such as PBAT or PLA).
The following chart shows world consumption of biodegradable polymers in 2020. Consumption is expected to increase significantly in 2020–25, driven by surging demand for biodegradable polymers in mainland China.
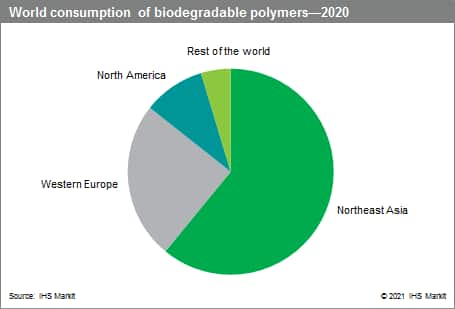
Northeast Asia—mainland China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan—is now the world’s largest producer and consumer of biodegradable polymers. Mainland Chinese capacity for biodegradable polymers has expanded significantly since 2017, driven mainly by legislation designed to reduce the volume of plastic waste. Additional expansion—especially of PLA and PBAT capacity—is expected during 2020–25, assuming that adequate supplies of feedstocks such as 1,4-butanediol, lactic acid, and lactide are available.
Western Europe remains a major producer and consumer of biodegradable polymers. Legislation is an important market driver; key initiatives include plastic bag bans in Italy and France, and EU waste disposal laws that limit the disposal of organic waste in landfill and allow the collection of biodegradable and compostable packaging with organic waste. The EU’s Single-Use Plastic Directive—which limits the uses of disposable cups, plates, food containers, drinking straws, and other items—has the potential to drive additional demand for biodegradable polymers.
Starch compounds, PLA, and PLA compounds accounted for the bulk of global biodegradable polymers consumption in 2020. The food packaging, dishes, cutlery, and bags market was the largest end-use segment, as well as the major growth driver for biodegradable polymers consumption.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Biodegradable Polymers is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Biodegradable Polymers has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- S&P Global | Biodegradable Polymers
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















