Published August 2024
para-Xylene (PX) is a C8 aromatic compound that is used exclusively as an intermediate feedstock for polyester production via purified terephthalic acid (PTA) or dimethyl terephthalate (DMT). PX is one of the most widely used aromatic compounds accounting for almost 86% of the total mixed xylenes demand, which was on a par with global benzene demand in 2023. PX is extracted from a mixed xylenes stream, which is commonly derived from crude oil sources like reformate and pygas. The major source of mixed xylenes and hence isolated PX is from refinery reformers, which accounted for around 60% of mixed xylenes production in 2023. Asia is the hub of PX production, hosting the largest share of the world’s total capacity in 2023. In the past 10 years, overall PX capacity has grown robustly on a global level; however, regional PX industries experienced massively contrasting growth. Asia and the Middle East aggressively added new capacity while developed regions like North America and Europe underwent the consolidation of inefficient units, leading to an increasing density of PX assets in Asia.
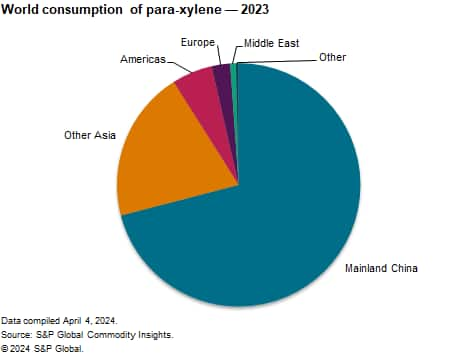
PX is a key raw material used in the production of purified terephthalic acid (PTA) and dimethyl terephthalate (DMT), which are used almost exclusively in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymer for the production of polyester fibers, PET solid-state resins and PET film. Over the past three decades, global PX demand has been driven by the extensive development of the polyester chain, which has occurred largely in Eastern Asia (including mainland China). The development of the Eastern Asian polyester industry has been driven primarily by the significant advancement of the regional textile industry, especially in mainland China. Production of polyester fibers is more labor intensive than traditional and heavily automated petrochemical manufacturing processes, and its production has developed rapidly where manpower costs were the most competitive and where the downstream textile industry was flourishing. Therefore, PX consumption has remained heavily dominated by Eastern Asia (including mainland China).
Most are international oil companies and national oil companies, or large refiners and petrochemical producers. The world’s largest PX producers are Saudi Aramco, China Petroleum Corporation (SINOPEC), Hengli Group and Reliance
PX consumption will continue to grow strongly, driven by increasing production of polyester fibers and PET solid-state resin; ultimately, the polyester value chain will benefit from the rising world population, changing lifestyles, and improvement in living standards, as well as the further economic development of emerging economies. Despite positive growth prospects for PX demand, the world average operating rate is forecast to decline to 70% during the forecast period because of the many upcoming new mainland Chinese capacities scheduled to come onstream.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – para-Xylene is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key Benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – para-Xylene has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















