Published December 2021
Phosgene is generated at the plant in which it is consumed in the production of p,p-methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) and “polymeric” MDI (PMPPI), toluene diisocyanate (TDI), polycarbonate resins, and others. Most phosgene is consumed in the production MDI and “polymeric” MDI (PMPPI). The MDI is used in reaction injection-molding (RIM) systems, thermoplastic resins (TPUs), high-performance elastomers, and spandex fibers, as well as having some use in coatings, adhesives, and sealants. The PMMI is used primarily in the production of rigid polyurethane foams and its main applications are for building and industrial insulation and refrigeration. Consumption of phosgene for MDI/PMPPI accounted for 55% of total demand in 2021. The second-largest consumption category is for TDI, which is used to make flexible polyurethane foams, packaging, and textiles. It accounted for 27% of total phosgene demand in 2021. Polycarbonate resin accounted for 13% of total phosgene consumption. Polycarbonate is used in industrial equipment parts and electronic components. All of the dominant consumption sectors are related to the automotive and construction industries that have been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. Demand for phosgene is expected to recover and grow at 4.3% per year during 2021–26.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of phosgene:
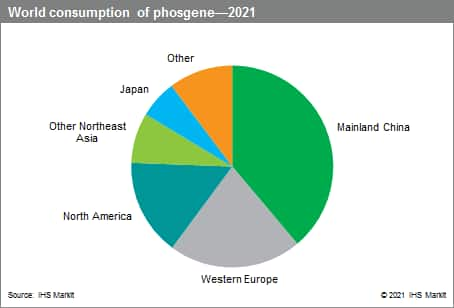
Demand for phosgene is generally driven by the global economy and its demand for automobiles, construction materials, packaging, electrical devices, appliances, and furniture. The use of phosgene technology in polycarbonate resin production is expected to decrease as more advanced and safer technologies for the production and processing of phosgene and its derivatives increase in this industry.
Mainland China is the largest phosgene-producing and consuming country in the world, representing 39% of total demand in 2021. Mainland China is expected to be the main consumer of phosgene over the next five years, with expected demand growth of about 6% per year. Western Europe follows with approximately 21% of global phosgene production and demand in 2021; this region is expected to have average demand growth of about 3% for the next five years. Most Asian countries consume polycarbonate resin; however, because of more use of phosgene-free technology, phosgene consumption will not grow as fast as production of polycarbonate.
The top-three phosgene producing companies are Covestro (24% of global capacity), Yantai Wanhua (22%), and BASF (18%).
Key findings and future implications for the phosgene market include the following:
- The TDI, MDI, and polycarbonate markets are expanding in or shifting to the Middle East and mainland China, as well as other Asian countries.
- Changes in manufacturing processes for polycarbonate resins to phosgene-free technology have moderated the phosgene growth potential in this application.
- Companies are beginning to emerge that specialize in phosgenation technology, which is phosgene production and reactions, and phosgene derivatives.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Phosgene is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key Benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook – Phosgene has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















