Published April 2022
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET) solid-state resins belong to the broad generic class of high-molecular-weight condensation polymers known as thermoplastic polyesters. They are derived from PET melt-phase resins (also referred to as polyester melt) that are further polymerized (solid-stated) before use and therefore have a higher intrinsic viscosity. The combination of good physical, optical, and lightweight properties has allowed PET solidstate resins to gradually displace glass bottles and containers, and it remains the material of choice for these applications. This report concentrates primarily on the supply/demand for PET solid-state resins used in bottle and packaging applications.
Over the past decade, PET solid-state resin consumption has increased by almost 50%. PET resin consumption has benefitted from the substitution of heavy-walled glass containers, especially in the beverage market, and has grown at a high rate. In developed markets, PET consumption is maturing as most glass substitution has already taken place; however, in developing regions, PET resin markets are still growing, as a result of increasing GDP, changing lifestyles, and improving living standards, as well as expanding populations. Mainland China accounted for nearly one-fourth of the global PET resin consumption in 2021; consumption has grown more than 4.0% per year from 2016 to 2021. The Indian Subcontinent and Africa have had significant demand growth, while mature markets such as North America and Western Europe have had stagnating and even decreasing consumption of PET resins.
The following pie chart shows world consumption of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) solid-state resins:
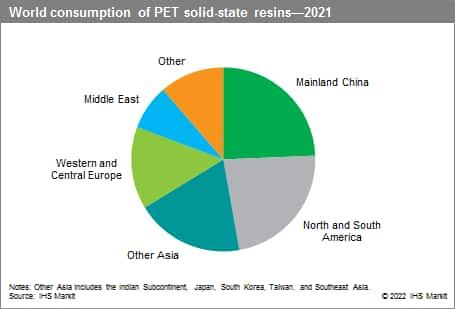
Global consumption of PET resin is led by the production of beverage containers, followed by food containers and cosmetic and pharmaceutical applications. Other PET applications such as film and sheet account for the remainder, driven primarily by developments in mainland China and the Middle East. Each region has certain preferences.
In developed regions, PET resin consumption has been affected negatively by several trends—the lightweighting of plastic bottles, the shift in consumer behavior toward lower consumption of carbonated soft drinks, and the increasing use of recycled PET (R-PET) material. The strong growth of R-PET demand has been driven primarily by legislation requiring the reduction of solid waste. Although the production of R-PET has increased over the past decade, it still represented only a small fraction of total global PET solid-state resin production in 2021.
Future growth in PET solid-state resins consumption will continue to be driven by the two largest end-use segments, beverage containers and other. As most of the glass substitution has already been achieved, PET resin consumption is currently driven primarily by the general growth of the beverage industry (containers). As such, the market is now driven heavily by emerging economies where the growing population, the improvement of living standards, and progressive westernization are driving the consumption of more bottled beverages.
For more detailed information, see the table of contents, shown below.
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook –Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Solid-State Resins is the comprehensive and trusted guide for anyone seeking information on this industry. This latest report details global and regional information, including
Key benefits
S&P Global’s Chemical Economics Handbook –Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Solid-State Resins has been compiled using primary interviews with key suppliers and organizations, and leading representatives from the industry in combination with S&P Global’s unparalleled access to upstream and downstream market intelligence and expert insights into industry dynamics, trade, and economics.
This report can help you
- Identify trends and driving forces influencing chemical markets
- Forecast and plan for future demand
- Understand the impact of competing materials
- Identify and evaluate potential customers and competitors
- Evaluate producers
- Track changing prices and trade movements
- Analyze the impact of feedstocks, regulations, and other factors on chemical profitability


















